Prerequisites
You should already have your domain(s) configured and working on Nginx and accessible in the browser. If you haven’t configured Nginx yet, please see Guide: Installing Nginx on Ubuntu 16.04 / 17.10
Cloudflare Users: Note that you don’t need Let’s Encrypt and can instead use Cloudflare’s own shared Universal SSL certificate and an Origin CA. If you want to keep Cloudflare and also use Let’s Encrypt, you must Pause Cloudflare now, otherwise it will interfere with certificate deployment. Once the Let’s Encrypt cert is deployed, you must unpause and set SSL to Full (Strict) in the Cloudflare crypto settings, otherwise you will get a redirect loop error.
1. Install Let’s Encrypt client (Certbot)
UPDATE FEB 2019: This article has been updated to reflect Let’s Encrypt’s end of TLS-SNI-01 support.
Let’s begin by updating the package lists and installing software-properties-common. Commands separated by && will run in succession.
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install software-properties-commonNow add the repositories universe and certbot.
sudo add-apt-repository universe && sudo add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbotPress ENTER if prompted.
Update the package lists again and install certbot for Nginx. This is the Let’s Encrypt client.
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install certbot python-certbot-nginxPress y and ENTER when prompted to continue.
2. Configure the Firewall
If you haven’t already done so, it is recommended that you enable the ufw firewall and add a rule for Nginx. Before enabling ufw firewall, make sure you add a rule for SSH, otherwise you may get locked out of your server if you are logged in remotely.
sudo ufw allow OpenSSHNow add the “Nginx Full” profile and then delete the redundant “Nginx HTTP” profile if it exists.
sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full'sudo ufw delete allow 'Nginx HTTP'You can check the current firewall rules with:
sudo ufw statusWe should now see our SSH and Nginx rules:
Status: active
To Action From
-- ------ ----
OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere
Nginx Full ALLOW Anywhere
OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Nginx Full (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 3. Get an SSL Certificate
We will now obtain a cert for our test domain example.com. Certbot has an Nginx plugin, which automates the certificate installation.
sudo certbot --nginxEnter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to
cancel):Enter an email address where you can be contacted in case of urgent renewal and security notices.
Please read the Terms of Service at
https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must
agree in order to register with the ACME server at
https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(A)gree/(C)ancel:Press a and ENTER to agree to the Terms of Service.
Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier
Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit
organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about EFF and
our work to encrypt the web, protect its users and defend digital rights.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(Y)es/(N)o:Press n and ENTER to not share your email address with EFF.
Which names would you like to activate HTTPS for?
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
1: example.com
2: www.example.com
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Select the appropriate numbers separated by commas and/or spaces, or leave input
blank to select all options shown (Enter 'c' to cancel):If you have multiple domains already configured on your server, you will see a list of them here. In this example, we only have one domain example.com and its www. prefix.
Select option 1 if you don’t want to use the www. prefix in your website address, otherwise select option 2.
Obtaining a new certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for example.com
Waiting for verification...
Cleaning up challenges
Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/example.com
Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the webserver configuration.
2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for
new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this
change by editing your web server's configuration.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel):Press 2 and ENTER to redirect all traffic to HTTPS.
Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://example.com
You should test your configuration at:
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=example.com
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -You’re done!
4. Test SSL
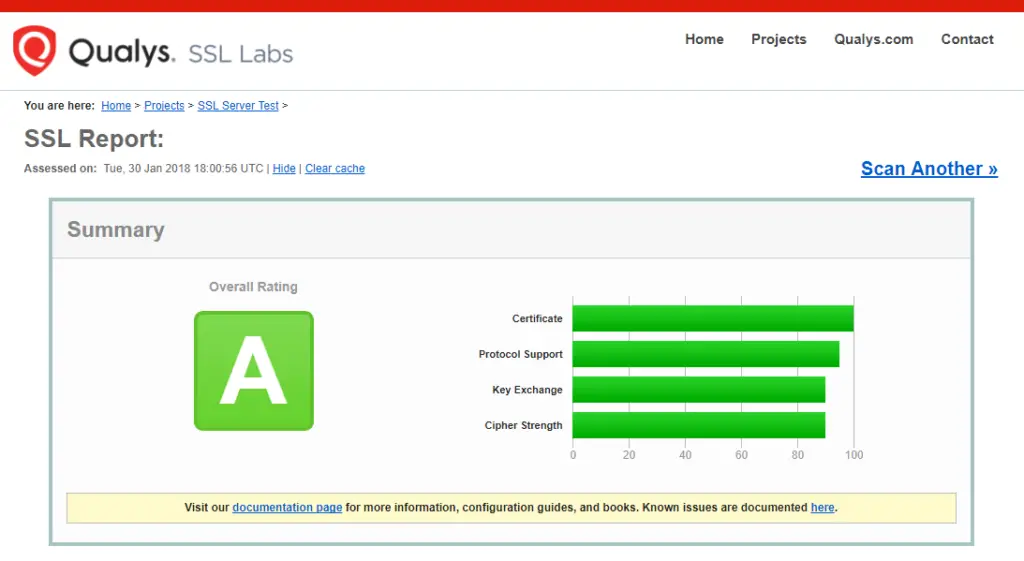
You can now go to ssllabs.com/ssltest/ and run an SSL test on your domain.
A successful test should receive an A rating.
5. Auto Renewal
As Let’s Encrypt certs expire after 90 days, they need to be checked for renewal periodically. Certbot will automatically run twice a day and renew any certificate that is within thirty days of expiration.
To test that this renewal process is working correctly, you can run:
sudo certbot renew --dry-runCloudflare Users
Please ensure your Cloudflare SSL settings are correct. Log in to Cloudflare, go to Crypto and make sure SSL is set to Full (Strict)
Let me know if this helped. Follow me on Twitter, Facebook and YouTube, or 🍊 buy me a smoothie.
What are the steps and considerations for Cloudflare users who choose not to use Let’s Encrypt and opt for Cloudflare’s shared Universal SSL certificate and an Origin CA instead? Additionally, why is it necessary to pause Cloudflare during the Let’s Encrypt certificate deployment, and what actions must be taken after the deployment to avoid redirect loop errors?
Checking the site in Chrome, it’s stuck in a redirect loop.
This page isn’t working
http://www.example.com redirected you too many times.
Try clearing your cookies.
ERR_TOO_MANY_REDIRECTS
Do you have Cloudflare enabled for that domain? If so, log in to Cloudflare, go to Crypto and make sure SSL is set to Full (Strict)
OK, it all works fine until I run
certbot renew --dry-runRunning post-hook command: systemctl start nginx
Hook command “systemctl start nginx” returned error code 1
Error output from systemctl:
Job for nginx.service failed because the control process exited with error code. See “systemctl status nginx.service” and “journalctl -xe” for details.
I check service status with
sudo systemctl status nginx.service“Failed to start A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server.”
I try restart Nginx:
sudo systemctl restart nginx“Job for nginx.service failed because the control process exited with error code. See “systemctl status nginx.service” and “journalctl -xe” for details.”
The things is, the site is still up and working. Just getting these errors.
This appears to be a bug with Certbot. You will need to force Nginx to restart.
sudo rebootEdit the renewal config. Its filename with depend on your domain. Check this folder
ls /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/Then open the file you have in there. e.g.
sudo nano /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/example.com.confThen comment out the line
installer = nginxso it looks like# installer = nginxSave and close.
Now try running
certbot renew --dry-runagain.It works. Thanks.
I can’t get it to install the cert 🙁 “Client with the currently selected authenticator does not support any combination of challenges that will satisfy the CA.”
This is a recent security issue but there is a fix. Please see article Help! Let’s Encrypt Error: “Client with the currently selected authenticator does not support any combination of challenges that will satisfy the CA.”