Introduction
Kali Linux is a specialized Linux distribution for ethical hacking, penetration testing, and digital forensics. A Kali Linux Live USB lets you run Kali on almost any computer without permanent installation.
This guide shows how to build a Kali Linux Live USB that can save changes between sessions (persistence), plus optional LUKS encryption for extra security.
Recommended USB Drive & Persistence Size
- Capacity: For basic use, 8–16GB is often enough. If you plan to store larger files or use more tools, aim for 32GB+.
- Persistence Partition: If you want a large persistence partition (e.g., 16GB+), ensure your USB has enough space for both the Live image and that partition.
- Performance: Huge partitions can slow down read/write speeds on older USBs. Encryption also adds overhead—larger partitions take longer to format and open.
- Optional Extra Partition: You could leave space for a FAT/NTFS partition if you need cross-platform file sharing.
1. Download Kali Linux ISO
Grab the latest Kali Linux Live ISO from the official Kali website. Choose the correct architecture for your system:
- x86_64 (Intel/AMD) for most PCs and older Intel Macs
- Apple Silicon (ARM64) for M1/M2 Macs
For stability, use the “Point Release Live Image” (e.g., Kali 2024.4). Weekly images are more up-to-date but less tested. If possible, use torrents for faster downloads.
Optional (Recommended): Verify the ISO
Because Kali is a security-focused distribution, it’s good practice to verify the downloaded ISO. Check the official Kali docs for details on validating checksums or GPG signatures to ensure the image hasn’t been tampered with.
2. Create a Kali Live USB
After downloading the Kali Linux ISO (and optionally verifying it), the next step is to write it to a USB drive. This creates a bootable “Live” environment that you can run on most PCs or Macs without installing Kali permanently. Below are methods for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
2.1 Windows: Rufus
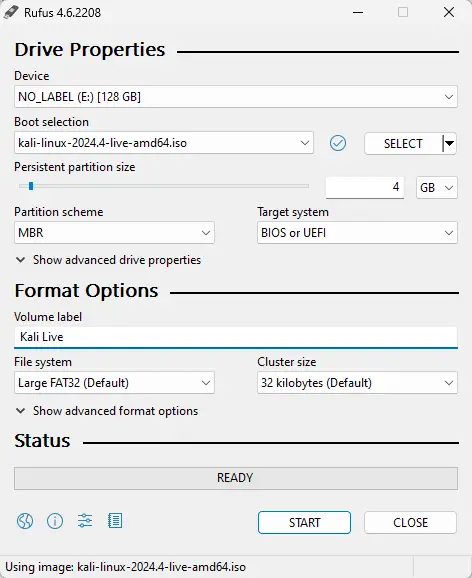
Rufus is a user-friendly tool for Windows that can create a Kali Live USB. If you want persistence, Rufus can set that up automatically during this step.
- Download and open Rufus.
- Select your USB under “Device.”
- Click SELECT and choose the Kali Linux Live ISO.
- If desired, set a “Persistent partition size” (e.g., 4GB) for automatic persistence.
- Click START and confirm any prompts.
- When Rufus finishes, eject the USB.
If you forgot to set persistence or used another tool, see Step 4 to add or fix persistence later.
2.2 macOS & Linux: Balena Etcher (GUI)
Balena Etcher is a cross-platform tool for flashing OS images. On macOS and Linux, Etcher does not create a persistence partition automatically, so you’ll need to set it up manually (see Step 4).
- Download/install Balena Etcher.
- Insert your USB drive (8GB or larger).
- Open Etcher and choose “Flash from file”, selecting the
Kali Live ISO. - Pick your USB drive as the target, then click Flash.
- When done, safely eject the USB.
2.3 macOS & Linux: dd (CLI)
If you prefer the command line, you can use dd to write the ISO directly to the USB. This also doesn’t create persistence automatically, so you’ll need to add it later (see Step 4).
- Identify your USB (e.g.,
/dev/sdbor/dev/disk2) vialsblk,fdisk -l(Linux), ordiskutil list(macOS). - Unmount the USB (
sudo umount /dev/sdb*on Linux ordiskutil unmountDisk /dev/disk2on macOS). - Write the ISO:
sudo dd if=/path/to/kali.iso of=/dev/sdb bs=4M status=progress
(Adjustof=as needed.) - Finish & Eject:
Runsyncthen remove the USB.
3. Boot and Test Your USB
Now that you’ve created your Kali Live USB, the next step is to boot from it and confirm it works. This usually involves changing your system’s boot order or using a one-time boot menu. Below are general guidelines for both PCs and Macs.
3.1 Windows & Linux: BIOS/UEFI
- Power on or restart your PC. During startup, press the key for your system’s boot menu or BIOS/UEFI settings (often F2, F12, Esc, or Delete).
- In the boot options, select your USB drive. It may be listed by its brand or as “USB HDD.”
- Save and exit. Your system should reboot from the USB and show the Kali boot menu.
- Alternate (Windows 10/11): Hold Shift while clicking “Restart” to open Advanced Startup. Then go to Use a device → USB.
- Tip: Some PCs have a dedicated one-time boot menu key (e.g., F9 on HP). Use that to boot from USB without permanently changing BIOS settings.
3.2 macOS Boot
- Insert the USB drive.
- Reboot your Mac. Immediately press and hold the Option (Alt) key.
- Select “EFI Boot” or “Windows” (the name can vary) when the boot options appear.
Apple Silicon (M1/M2): Shut down your Mac, then press and hold the power button until the startup options screen appears. Choose your USB drive to boot from it.
3.3 Test Persistence (If Configured)
When Kali’s boot menu appears, you’ll typically see:
- Live system (amd64)
- Live system (amd64) fail-safe mode
- Live system (amd64) forensic mode
- Live system with USB persistence
- Live system with USB encrypted persistence
- Start installer
- Advanced install options
- Utilities
If you used Rufus to create a persistence partition, select “Live system with USB persistence.” Once on the Kali desktop, create a test file (e.g., on the Desktop), then reboot and pick the same persistence option. If the file remains, persistence is working!
If you did not set up persistence yet, just choose “Live system (amd64)”.
Default Credentials: The default username is kali, and the password is kali. To become root, use sudo su.
4. Manually Adding Persistence
Some tools—like Rufus on Windows—can create a persistence partition automatically, but others (Etcher, dd, etc.) do not. If you didn’t enable persistence or used a tool that lacks this feature, you can still manually add persistence to your existing Kali USB. The basic idea is to create a second partition labeled persistence, format it to ext3 or ext4, and add a configuration file so changes are saved across reboots.
4.1 Key Requirements
1. You generally cannot modify a USB while you’re booted from it if the main partition is read-only (e.g., the Kali ISO partition). You’ll need a second environment—a different USB, a VM, or another computer—so your target USB isn’t in use.
2. You need a tool that can shrink the main partition and create an ext3 or ext4 partition labeled persistence. Windows Disk Management and macOS Disk Utility generally cannot do this because of the read-only ISO partition and lack of native ext3/ext4 support.
4.2 Windows Users
Option A: Rufus (Automatic)
If you created your USB in Windows using Rufus, you can select a “Persistent partition size” during the initial setup. That way, Rufus automatically creates persistence.
Option B: Manual Creation with MiniTool Partition Wizard
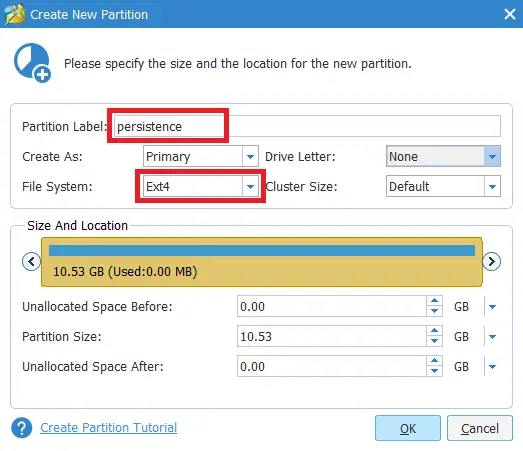
If you forgot to enable persistence in Rufus or used another tool, you can still add persistence manually. A popular free option is MiniTool Partition Wizard Free:
- Install MiniTool Partition Wizard (Free edition).
- Shrink the main partition (the one containing Kali) to free up space.
- Create a new partition in the unallocated space:
- Partition Type: Primary
- File System: Ext4
- Partition Label:
persistence
- Apply the changes, then safely remove the USB once it’s done.
After creating the partition, you’ll finalize it in Kali Live (see 4.6 Configure the Persistence Partition).
4.3 macOS Users
macOS Disk Utility generally can’t resize the read-only ISO partition nor format ext3/ext4. To add a persistence partition, you must use a Linux environment—for example, boot from another Linux USB, or use a Linux VM (e.g., VirtualBox or VMware) and pass the USB through to it. Then follow the steps in 4.5 Resizing/Creating a Partition to shrink and create the persistence partition.
4.4 Linux Users
If you have another Linux system (installed or a second Live USB), you can use GParted or parted to shrink the main Kali partition and create an ext3/ext4 partition labeled persistence. You’ll then configure that partition (see 4.6) so Kali saves data across reboots.
4.5 Resizing/Creating a Partition
Regardless of your operating system, the main steps to add persistence are:
- Shrink the existing Kali partition (the read-only ISO partition).
- Create a new
ext3orext4partition labeledpersistence.
Below are two common methods on Linux. For Windows, see MiniTool Partition Wizard (See 4.2 above), and for macOS, you’ll need a Linux environment or VM with GParted or parted.
Method A: GParted (GUI)
- Boot into a Linux environment where your target USB isn’t mounted.
- Run
sudo gpartedand select the USB (e.g.,/dev/sdb). - Shrink the existing partition, then create a new
ext3/ext4partition labeledpersistence. - Apply the changes. Note the partition name (e.g.,
/dev/sdb2).
Method B: parted (CLI)
If you prefer the command line:
sudo parted /dev/sdb(parted) print
(parted) resizepart 1 <new_end>
(parted) mkpart primary ext4 <start> <end>
(parted) set 2 lba off
(parted) quitExample Steps:
- Identify your USB device (e.g.,
/dev/sdb). printshows current partitions.resizepartshrinks the main partition.mkpartcreates a new partition for persistence.quitto apply changes.- Note your new partition name (e.g.,
/dev/sdb2).
4.6 Configure the Persistence Partition
Note: If you plan to encrypt this partition, you can skip this step and go straight to Step 5.
After creating the partition, label it persistence (if you haven’t already), then format it and add the persistence.conf file:
sudo mkfs.ext3 -L persistence /dev/sdb2
sudo e2label /dev/sdb2
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/my_usb
sudo mount /dev/sdb2 /mnt/my_usb
echo "/ union" | sudo tee /mnt/my_usb/persistence.conf
sudo umount /mnt/my_usbNote: Adjust /dev/sdb2 if your partition name differs (e.g., /dev/sdb3 or /dev/sdc2).
4.7 Reboot and Use Persistence
Reboot your system and choose “Live (amd64) USB Persistence”. If everything is set up correctly, any changes you make will now persist across reboots.
5. (Optional) Encrypt the Persistence Partition (LUKS)
Important: This will wipe data in your persistence partition, so back up any important files first.
5.1 Identify the Correct Partition
If you already know the persistence partition (e.g., /dev/sdb2), skip to Step 5.2.
Otherwise, run:
sudo fdisk -lYou’ll see one larger FAT32 partition for the “Live” system and a smaller 83 Linux partition for persistence. For example:
Output:
Disk /dev/sdb: 115.7 GiB, 123480309760 bytes
...
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sdb1 2048 34603007 34600960 16.5G c W95 FAT32 (LBA)
/dev/sdb2 34603008 42969087 8366080 4G 83 LinuxHere, /dev/sdb2 is the persistence partition. If you don’t see it, go back to Step 4 and create one first.
5.2 If the Partition Is Currently Mounted (e.g., Rufus)
If you created this USB with Rufus and booted “Live system with USB persistence,” the persistence partition is auto-mounted, so cryptsetup will fail (“device in use”). To fix this, you need to prevent Kali from mounting it on reboot:
- Rename the partition label (e.g.,
sudo e2label /dev/sdb2 old_persist). This stops Kali from recognizing it as a persistence partition on reboot. - Reboot into a non-persistent session (e.g., “Live system (amd64)”) so the partition is not in use.
- Now the partition is free. Proceed to Step 5.3 to encrypt it.
5.3 LUKS Format & Configuration
Step 1: Initialize LUKS, where /dev/sdb2 is your own persistence partition:
sudo cryptsetup --verbose --verify-passphrase luksFormat /dev/sdb2Type YES (in capitals) to confirm, then pick a secure passphrase. (If needed, generate a passphrase here).
Step 2: Open the container:
sudo cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/sdb2 my_usbEnter your passphrase.
Step 3: Format & create persistence.conf:
sudo mkfs.ext3 -L persistence /dev/mapper/my_usb
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/my_usb
sudo mount /dev/mapper/my_usb /mnt/my_usb
echo "/ union" | sudo tee /mnt/my_usb/persistence.conf
sudo umount /mnt/my_usb
sudo cryptsetup luksClose my_usbReboot and choose “Live system with USB encrypted persistence.” Enter your LUKS passphrase on boot. Your data is now protected.
User Feedback & Common Issues
Over time, this guide has received many comments—some for older Kali versions. Below are common issues and tips:
- Partition Label Must Be “persistence”
Ensure the partition label is exactlypersistence. - Password/Keyboard Layout
LUKS passphrases can fail if you switch keyboards. Use a simple passphrase with lowercase/numbers only to avoid issues. - Stuck at “Please unlock disk /dev/sdb2”
Some older builds had encryption bugs. Update Kali or try another USB brand. - “Failed Unmounting /run/live/medium” or “/tmp”
Disabling Secure Boot or using Legacy BIOS can help. Some USB sticks are incompatible. - Resize Errors/“Invalid Config File”
Some Windows tools fail on certain USBs. Wiping partitions withdiskpartor GParted can fix it. - Data Only Saves in Persistence Partition
Make sure you’re booting “(Encrypted) USB Persistence.” Thepersistence.confmust have/ union. - Sluggish Performance on Large USBs
Use USB 3.0 or consider a full Kali install on USB if speed is critical.
Conclusion
You now have a Kali Linux Live USB that supports persistence and optional LUKS encryption. Whether you’re on Windows, macOS, or Linux, you can create a portable pentesting environment. If you get stuck, consult the official Kali docs or leave a comment below!
Let me know if this helped. Follow me on Twitter, Facebook and YouTube, or 🍊 buy me a smoothie.

Thanks a lot this helped me😁
I think this is a fantastic tutorial!
It almost worked perfectly for me. Every time I wrote the ISO to the USB it would create an ISO9660 format for the two partitions. Gparted wouldn’t let me extend these partitions so I had to create an additional partition alongside the primary two. I used this command…
fdisk –wipe=never -t dos /dev/sdX
(Follow dialogs, but “n” for the new partition and I used default configurations. Then the “w” option to write the changes to the USB.)
…as suggested in Vojtech Trefny’s reply.
https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/618615/create-another-partition-on-free-space-of-usb-after-dd-installing-debian
I was able to jump back into your tutorial at Step 3 after creating this partition, and I just targeted this partition as the one to be encrypted. I thought I’d mention it in case you wanted to add a 2.5 step or something.
Looks like there are changes on the kali live 2022.1 or Im wrong?
Hello, I used 64 GB pendrive to and used 50 GB persidtance, then i install application like terminator. but application getting deleted after restart. also settings are restored to default.
Good news. And I think you can add a part of creating new sdb3. Also, it will be good to hear your news about making a standalone Kali installation on a usb drive, full encrypted, the part which I can’t deal with. Thank you big guy.
I can not create persistence partition over 4GB. It is possible?
How big is your USB stick?
Is it 16 GB?
Hello, Thanks for your great tutorial.
I made a massive mistake, I used my_sub instead of my_usb and now no file or folder saves in desktop.
How can I remove this persistence and make another one or what else should I do -_-
Just use win + r and type “diskpart”, then type “list disk” and type “select x” x is your usb number according to the list disk output. Then type “clean” and now go to “this pc” and format the usb with default parameters.
worked for me. Thank’s a lot!
Kali Live 2021.3 won’t boot with Dell Alienware m17 R4 from USB. Secured Boot is disabled. UEFI is enabled.
Disable uefi worked for me
Hi thanks for all it worked! (I made the Live USB Persistence without encryption)
I have a simple question. I get logged in automatically everytime without any login screen. Is there a way to make a login screen for the login so i can put in my USER and my Password ?
Thanks!